Hypertention
₹799.00 – ₹999.00
- Online Available in All India.
- Home Visit Available Only In Kolkata.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition that occurs when the pressure in your blood vessels is persistently too high. It’s defined as a systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 130 mm Hg or higher, or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 80 mm Hg or higher.
Description
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition that occurs when the pressure in your blood vessels is persistently too high. It’s defined as a systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 130 mm Hg or higher, or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 80 mm Hg or higher.
Hypertension can be serious if left untreated and can lead to many medical problems, including: Heart disease, Stroke, Kidney failure, Eye problems, and Aneurysm.
Hypertension is often called a “silent killer” because people with high blood pressure often don’t have any symptoms. The only way to know if you have high blood pressure is to get your blood pressure checked.
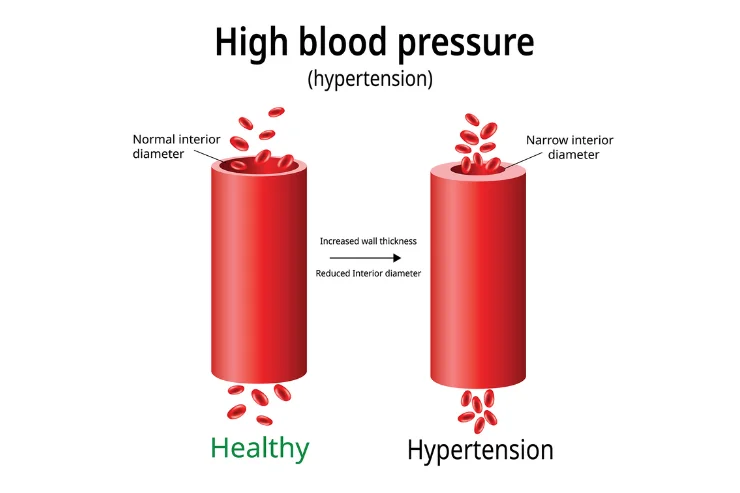
Some things that can increase your risk of developing hypertension include:
- Age
- Genetics
- Being overweight or obese
- Not being physically active
- High-salt diet
- Drinking too much alcohol
Can yoga exercise control Hypertension?
Yoga can help manage hypertension through a variety of practices, including:
- Pranayama and meditation
These practices can be done while sitting in a chair or in meditative poses like sukhasana, ardha padmasana, padmasana, or vajrasana. Slower breathing and heart rate can help lower blood pressure.
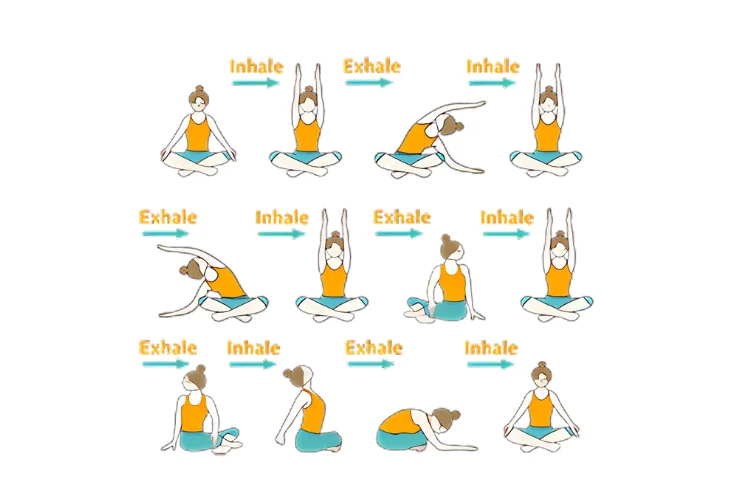
- Asanas
Some asanas that may help lower blood pressure include:
- Trikonasana (triangle pose)
- Balasana (child’s pose)
- Paschimottanasana (seated forward bend)
- Baddha Konasana (bound angle pose)
- Janu Sirsasana (head-to-knee pose)
- Virasana (hero pose)
- Savasana (corpse pose)
- Breathing techniques
Some breathing techniques that may help include:
- Bee breathing, which can help calm the mind
- Alternate nostril breathing
- Avoid certain poses and practices
Avoid poses that compress the front of the diaphragm, such as dhanurasana (bow pose) and mayurasana (peacock pose). Also avoid head stand (topsy-turvy) postures and hyperventilation breathing practices.